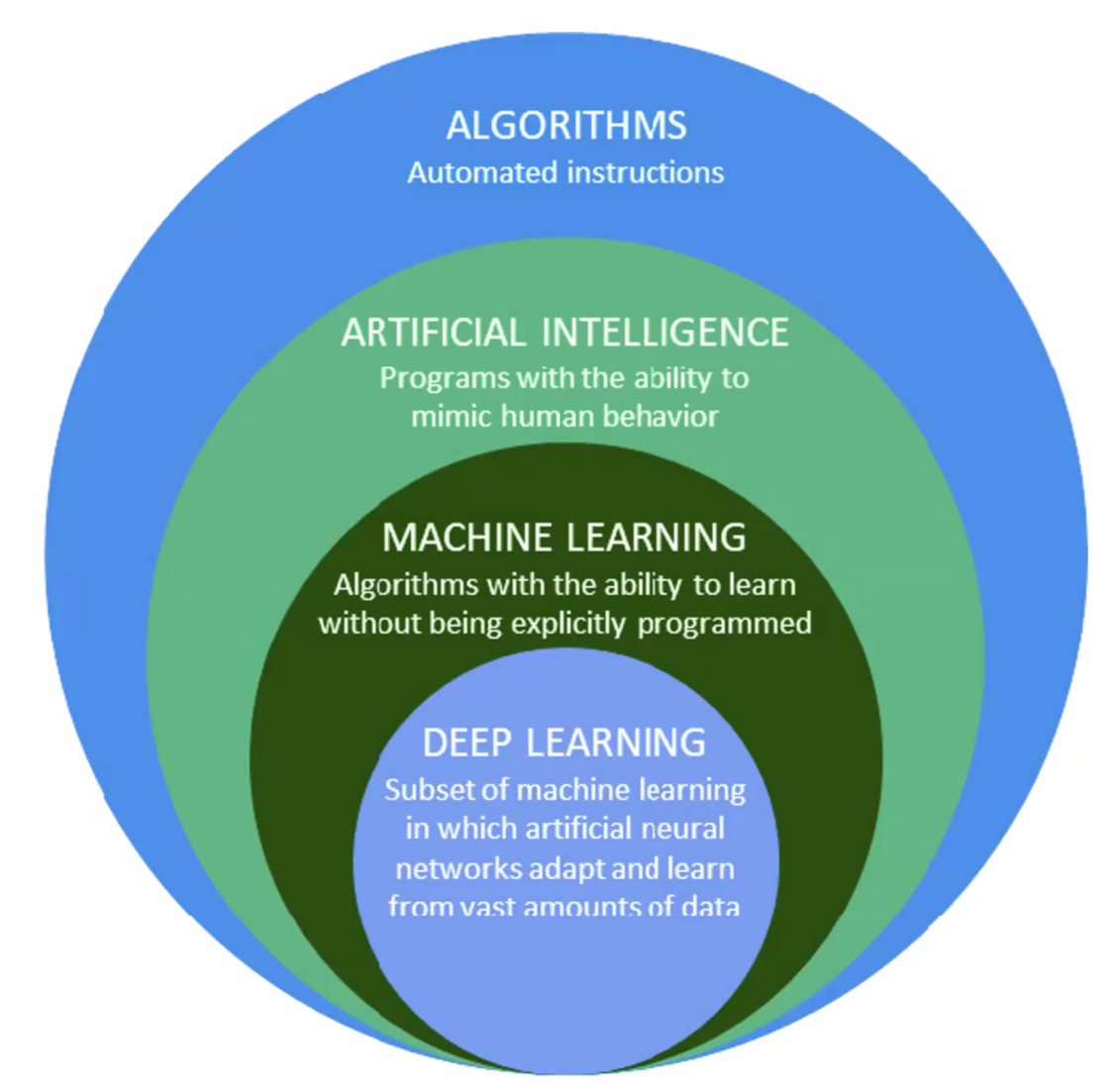
Towards Automated and Trustworthy Machine Learning
Definitions
-
What is learning?
- Observation --> Learning --> Skill
-
Skill: How to make decision (action)
- Classify an image
- Detect object
- Translate a sentence from one language to another
- Learn to play a game
- …
-
Machine learning: (Automatic the learning process) 传统的算法是给一些既定的算法或规则进行运算,根据环境的不同进行定制,机器学习就是希望机器能够自动归纳出决策的步骤。
- Data --> Machine Learning --> Skill (decision rules) 机器学习只需给定数据和算法就能自动化进行这样的流程。
Formalization
- input :
- output :
- target function to be learned:
- data:
- hypothesis (model) :
Machine Learning Problems
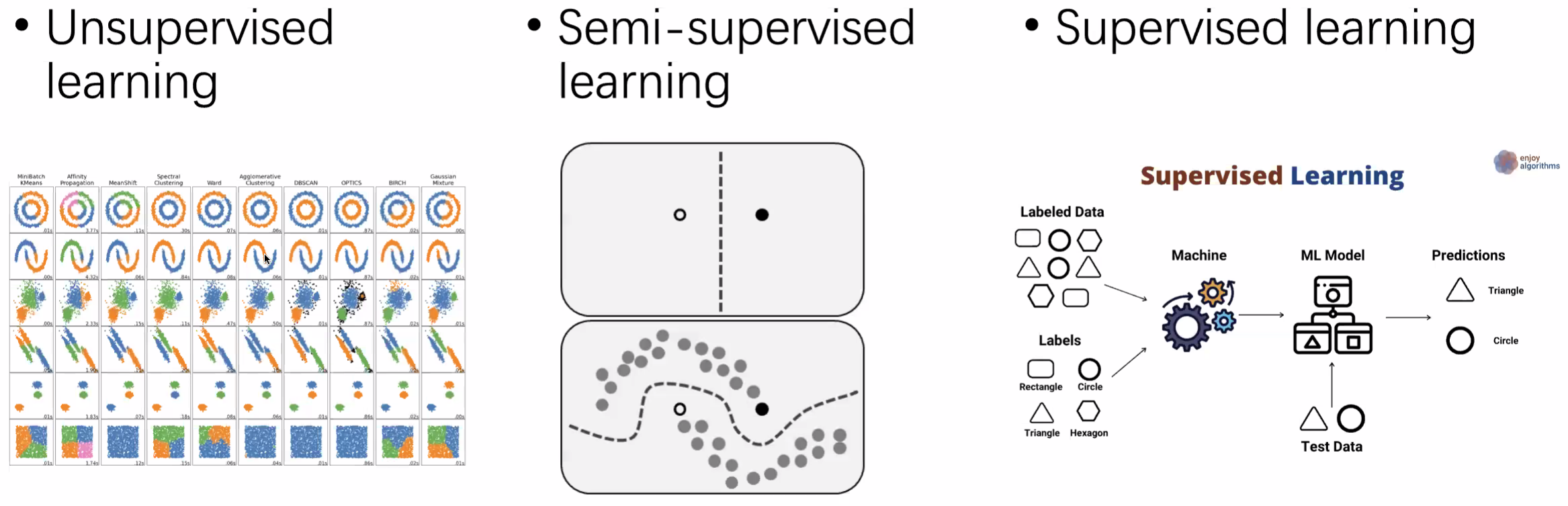
- Supervised Learning: every comes with (label)
- Unsupervised Learning: only , no 有两个数据簇(cluster),希望把这两个cluster分开
- Semi-supervised Learning: Some labeled data and some unlabeled data
- Transfer Learning: Transfer knowledge from source datasets to a target dataset 会下国际象棋,迁移到下中国象棋
Classical Questions
Binary Classification
credit: approve/ not approve
…
Regression
Stock price prediction
Movie rating prediction
Multi-class classification
object classification (MNIST, …)
Multi-label prediction
multi-class problem or multi-label
Document categorization
Document/image tagging
…
Extreme classification (large output space problems)
millions of billions of labels (but usually each sample only has few labels)
recommendation systems: predict a subset of preferred items for each user
document retrieval or search: predict a subset of related articles for a query
Structural prediction
POS in NLP: I (pronoun) love (verb) ML (noun)
Multicalss classification for each word (word --> word class)
not using information of the whole sentence
Structure prediction problem
sentence --> structure (class of each word)
Challenges : trustworthy & human effort
machine learning pipeline:
Data (SQL DB, Web Data, Cloud Sourcing,…)–> prepare Data --> build & train --> deploy
- What feature?
constraint / Rule, Budget, Efficiency
- Which model?
Linear Model (LR, SVM, …), Boosting Model (GBDT, RF, …), Neural Network (FC, Convolutional, Recurrent, …)
- Which parameter?
Hyperparameter, Optimizer
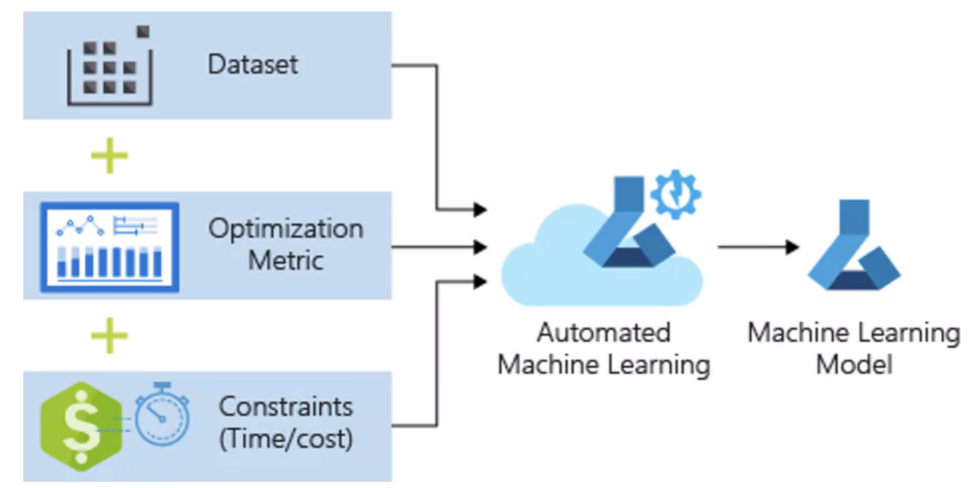
Automated ML
AutoML simplifies each step in the machine learning process,from handling a raw dataset to deploying a practical machine learning model.
Neural Architecture Search [ECCV’21, ICLR’21]
怎么选取一个比较好的神经网络?
-
both accuracy and efficiency
-
Evolutionary Algorithms (Miller et al 89, Schaffer et al. 92, Verbancsics & Harguess 13)
从已知选项中挑几个进行评估,通过某种技术获取更好的选项。无法保证一定能拿到更好的结果。
-
Bayesian Optimization (Snoek et al 12. Domhan et al 15)
-
Reinforcement Learning
RL通过一直增大Controller的结构可以保证得到一个更好的model
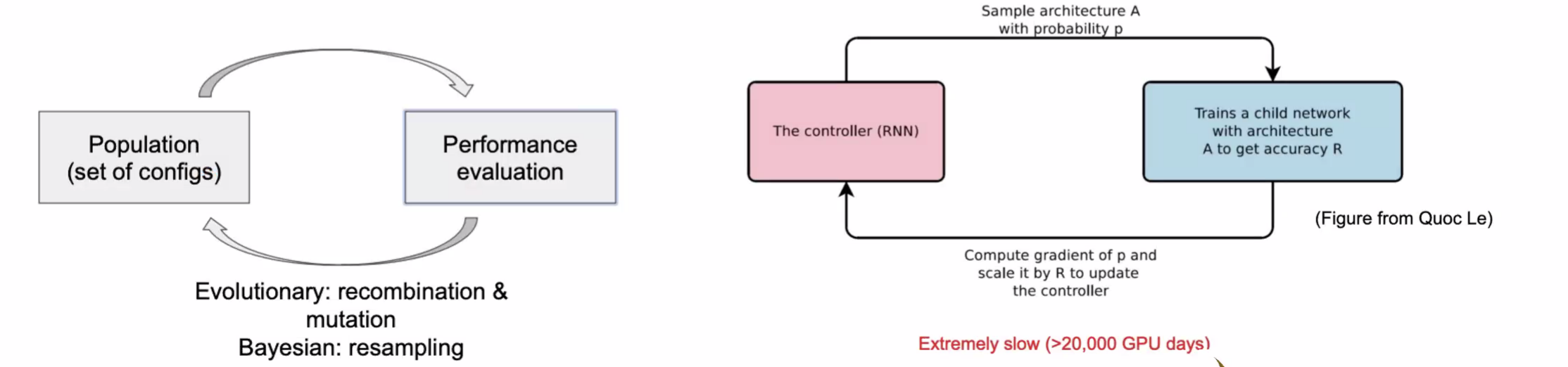
以上算法都很慢,因为每产生一个configs就要更新model,在每个迭代中要重新训练模型很多很多次,迭代太多开销特别大。
- Supernet: ensemble of many architectures
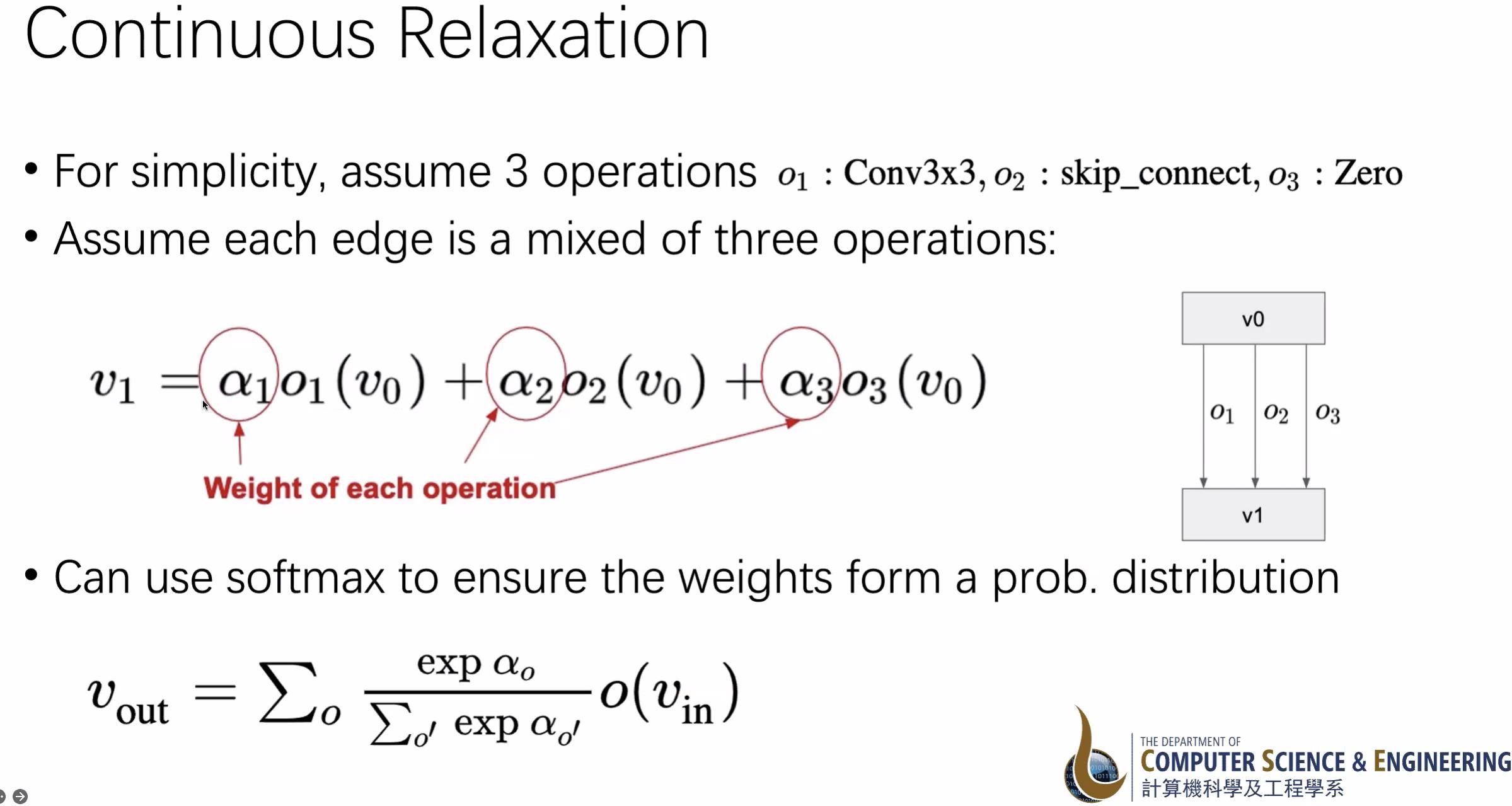
所有网络共享权重,先训练好再裁剪。是一种continuous relaxation (退化),把所有路径都加起来然后训练选择其中一个
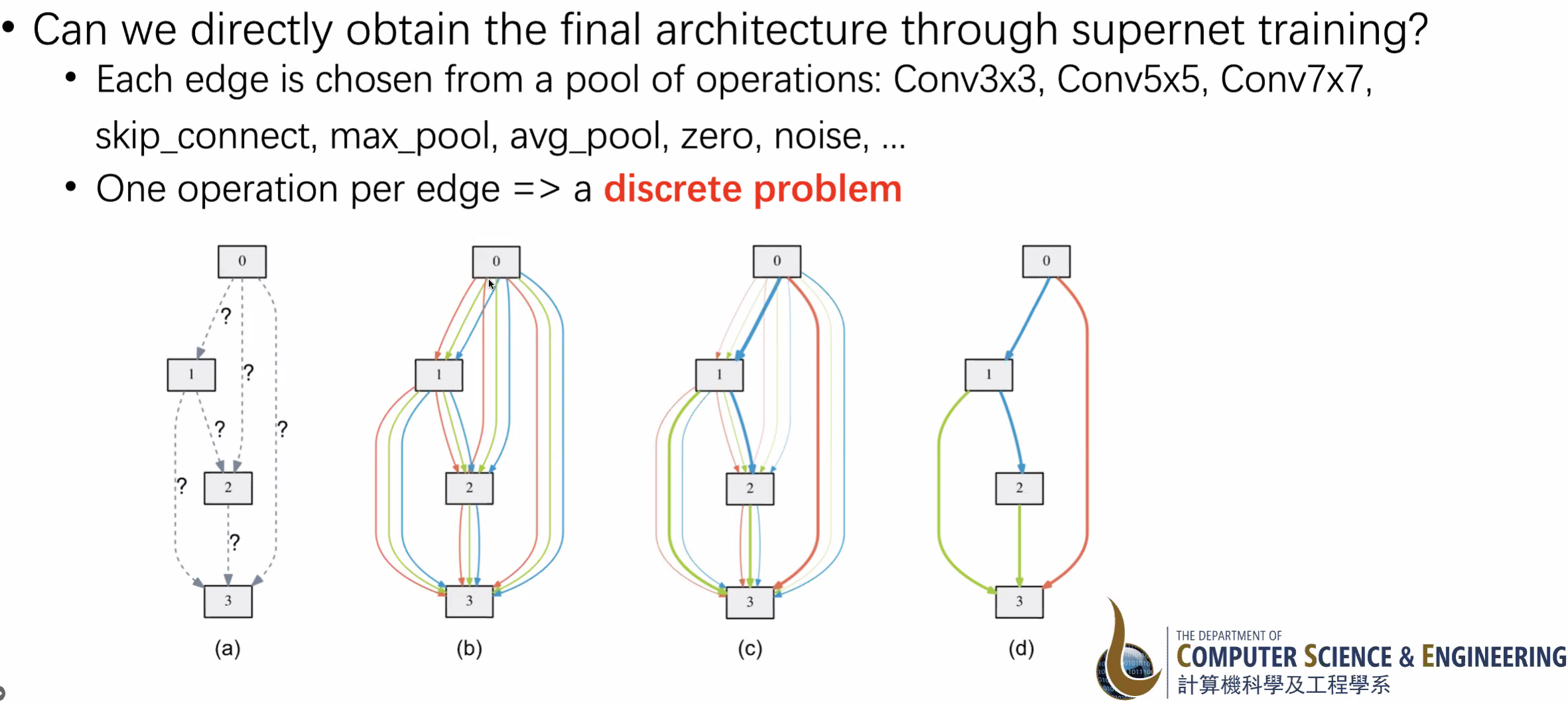
(b) is a supernet

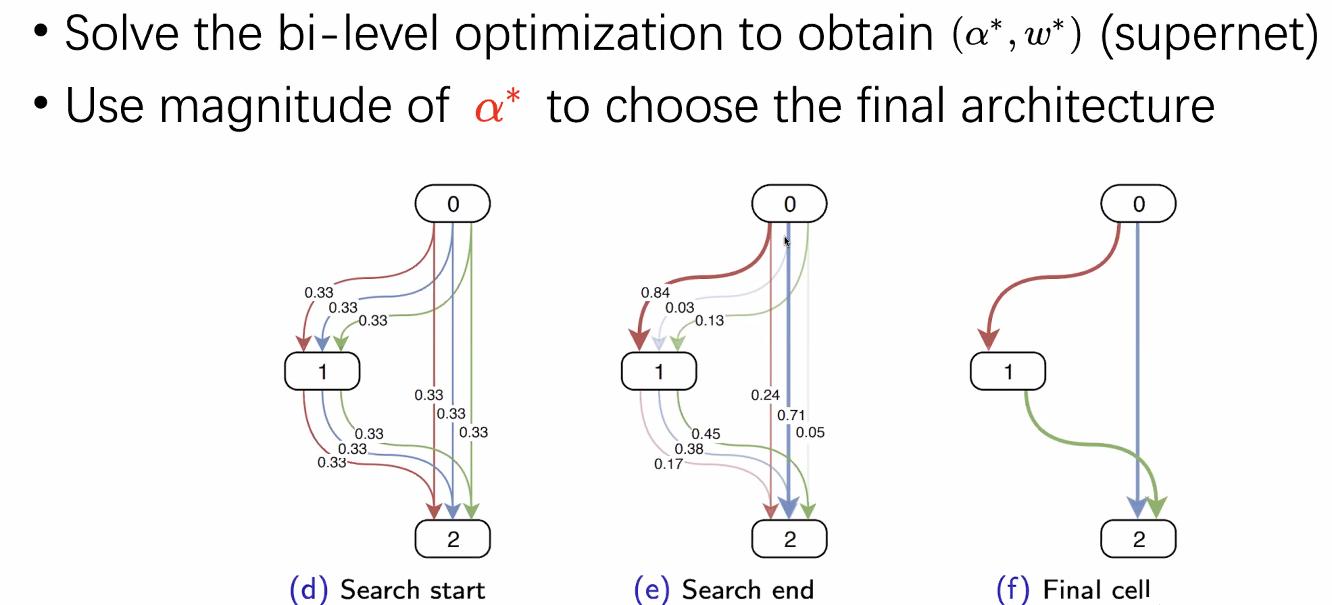
Bi-Level optimization tp obtain supernet.
Auto ML有哪些类型?
- NAS
- Hyperpatameter Optimization
- Meta learning and learn to learn
- Automated RL
- AutoML in Physical World
- …
目前只追求精度,不考虑其他信息。但也存在其他问题,比如精度不一定表明效果特别好。
examples:
-
Researchers trick Tesla Autopilot into steering into oncoming traffic。在路上贴三个点可以使特斯拉偏离方向;
-
ML炒股某时做出奇怪的决定导致大盘剧烈波动;
-
聊天机器人存在racism,奇怪翻译等。
因而可信化机器学习很重要
Trustworthy
-
Not alchemy
可解释性Explainability
鲁棒性Robustness
安全性Security
隐私性Privacy
公平性Fairness… -
Establish model understanding
Adversarial Robustness
目前的机器学习会被某些噪声影响
Stop sign + 0.001 * Noise = Stop sign (recognised of speed limit 40)
Accuracy Robustness
单独追求高精度AI可能导致一些trouble。
为什么鲁棒性重要?
机器学习会被采用在很多危险或敏感领域,机械臂,航空系统,。。。,如果不够鲁棒性可能会导致系统瘫痪或错乱,这是不可接受的;
鲁棒性可以指导我们构建更好的模型,有些工作利用对抗样本提升模型表现
为什么要研究可解释性?
可以看成是一种对模型的debug,现在很多神经网络没有这种能力;
对模型更好控制 get human-in-the-loop;
learn new insights,比如Alphago告诉我们一些新的特殊的下法,让我们更好的做一些任务,比如alphafold可以预测蛋白的结构和形成方式等
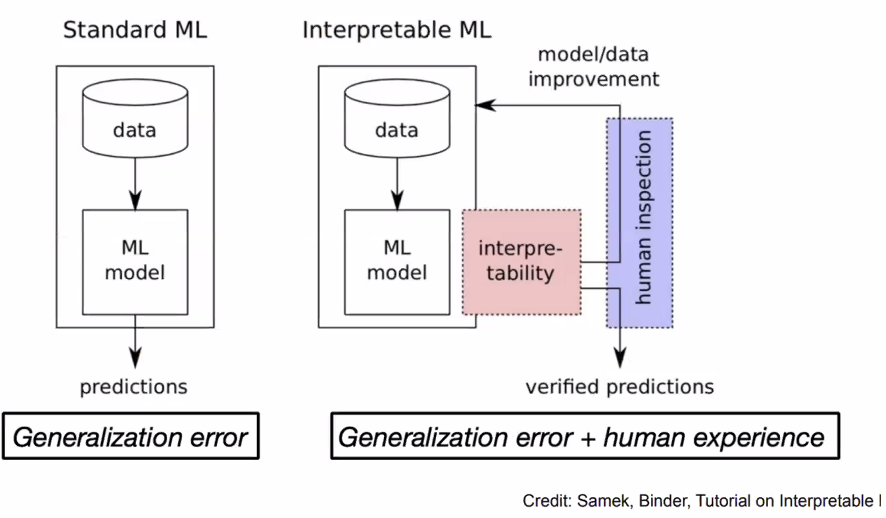
可解释性的应用:
-
Debugging
-
Bias detection
-
Provide recourse to individuals who are adversely affected by model predictions (比如信用卡被拒了之后可以给你一些建议让你之后能获批)
-
Assess if and when to trust model predictions
Useful Resources:
Deep Learning Book: www.deeplearningbook.org
CS229: Machine Learning from Stanford
Open framework: sklearn, tensorflow, PyTorch
Questions:
机器学习的未来在于从大量有相似规律的数据中寻求规律,从而对未来可能会出现的情况进行预测,但是当没有足够的样本支撑的时候,机器学习的作用是不是就被缩小了,在这种情况下,机器学习如何在小样本甚至零样本的情况下进行学习,如何规避数据样本不足带来的负面影响?
ANS: Supervised Learning对样本要求很高,但是unsupervised learning或者reinforcement learning对样本数量要求很低。

